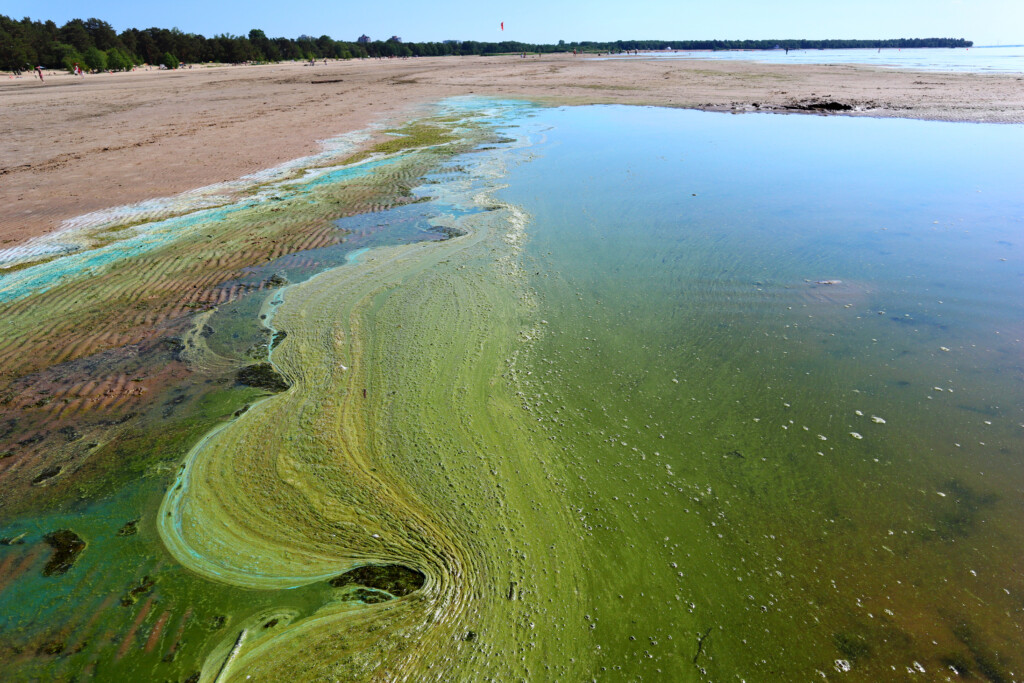
After several years in the making, HOLAS 3 thematic assessments on the state of the Baltic Sea have been published, covering the period of 2016–2021. The thematic assessments are part of the third HELCOM holistic assessment (HOLAS 3), providing a holistic view of the Baltic Sea ecosystem health.
The holistic approach highlights the interconnectedness of various environmental factors and their impact on the ecosystem. The five assessment reports each focus on a specific topic, addressing the state of biodiversity, environmental pressures, eutrophication, and the relationship between humanity and nature. The findings offer valuable insights for policymakers, scientists, and stakeholders alike.
The results of HOLAS 3 have been published in stages, commencing in March 2023, and the process will culminate in the publication of the summary report State of the Baltic Sea, expected at the end of October 2023.
A comprehensive holistic assessment on the state of the Baltic Sea is conducted once every six years. The reports result from collaborative efforts among HELCOM member states, scientific experts, and organizations dedicated to the protection of the Baltic Sea. They serve as a cornerstone of HELCOM’s work and policymaking, assisting in the monitoring of the implementation and the effectiveness of the Baltic Sea Action Plan (BSAP).
Thematic assessments 2023
HELCOM Thematic assessment of economic and social analyses 2016-2021
HELCOM Thematic assessment of spatial distribution of pressures and impacts 2016-2021
HELCOM Thematic assessment of biodiversity 2016-2021 (Main report compressed)