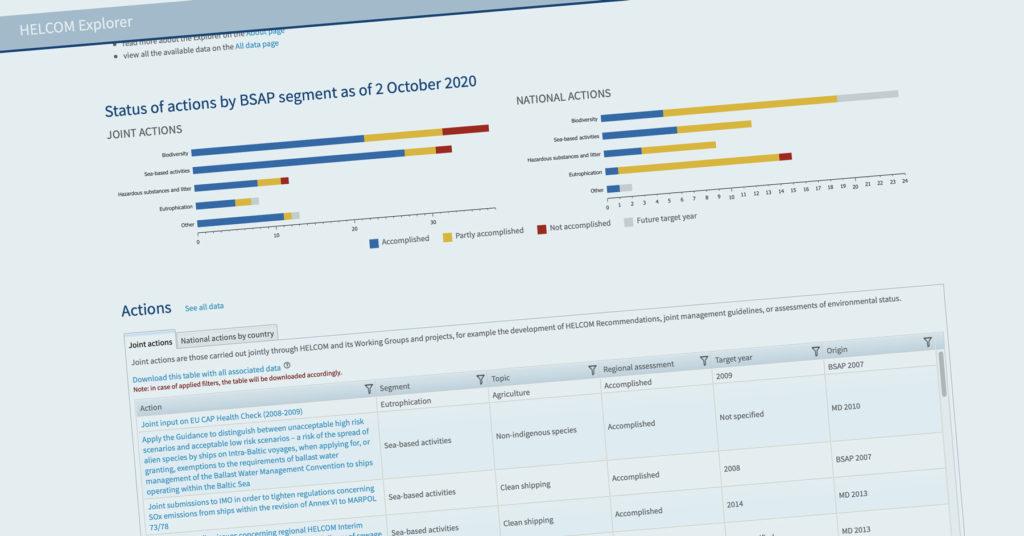
Entering a final stretch, another major milestone was crossed last week when the first full draft of the updated Baltic Sea Action Plan (BSAP) was presented to the organization’s decision-makers during the autumn meeting of the HELCOM Heads of Delegation (HOD 59-2020) that took place online.
Building on the existing plan, the updated BSAP is expected to maintain and adapt the current structure and segments that seek to reflect the pressures stemming from land (“Eutrophication” and “Hazardous substances and litter”) and from our activities at sea (“Sea-based activities”) as well as the state of the environment (“Biodiversity and ecosystems”).
In addition, the updated plan is due to feature a segment on horizontal actions having an incidence on the four main segments. These are climate change, monitoring, maritime spatial planning, economic and social analysis, and financing.
Furthermore, all measures and actions contained in the new plan are intended to be implemented by 2030 at the latest.
The updated BSAP is expected to be adopted by the Ministers of the HELCOM Contracting Parties during the HELCOM Ministerial Meeting that will be held in Lübeck, Germany on 20 October 2021.
With its set of targets for protecting biodiversity and reducing the pressures affecting the Baltic, as well as its number of concrete measures, the BSAP remains one of the most effective instruments for achieving the HELCOM ecological objectives, offering a long-term vision and strategic orientation for attaining good environmental status in the Baltic.
The original plan, adopted in 2007, can be credited with significantly reducing inputs of nutrients and hazardous substances, improving the protection of biodiversity, and boosting cleaner and safer shipping practices.
At HOD 59-2020, the decision-makers also approved a draft of the HELCOM Science Agenda that is meant to support the implementation of the BSAP and other HELCOM processes, by identifying the scientific knowledge needs related to the Baltic marine environment and which are foreseen to surface in the next 10 years.
Meant to be launched alongside the new BSAP, the first draft of the Baltic Sea Regional Nutrient Recycling Strategywas also presented during the meeting. In a bid to curb eutrophication, the strategy seeks to minimize the run-off of nutrients, stemming mainly from agricultural sources such as fertilizers, to the Baltic Sea by keeping them in a closed loop.
More good news: the Heads of Delegation announced the removal of HELCOM Hot Spot n°42, the Riga wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), from its list of pollution sites.
More than EUR 200 million were invested in the plant over the last 20 years, leading to a significant reduction of the discharges of nutrients and hazardous substances to the Baltic via the Lielupe river. The WWTP is now complying with EU regulations and almost fully meets the more stringent HELCOM targets on water purification.
The Riga WWTP had been added to the list of significant pollution sites due to insufficient treatment of wastewater and a large share of untreated municipal wastewater being released to the environment.
The HELCOM Heads of Delegation further approved the draft of a key regional instrument for fighting pollution incidents at sea, the Joint Inter-Regional Marine HNS Response Manual which will replace the current HELCOM Response Manual Volume II. A guideline for addressing and coordinating response to major accidents such as oil or chemical spills, the manual is expected to be adopted during the next meeting of the Helsinki Commission in March 2021.
On shipping, and more specifically on the management of ballast water which is a major source of introduction of alien species to the Baltic Sea, the Heads of Delegation further approved the revised HELCOM-OSPAR Joint Harmonised Procedure on the granting of exemptions under International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments (JHP).
The procedure is supported by an online decision tool that gives shipping professionals a quick overview of the risk of introducing non-indigenous species (NIS) through ballast water between two ports. Co-developed with OSPAR and recently updated, the tool covers both the North and Baltic Seas.
The collaboration between HELCOM and OSPAR comes at a time when both organizations are actively seeking to strengthen their partnership, a fact particularly welcomed during HOD 59-2020.
Experts from the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina also presented their recent discussion paper on underwater archaeology “Traces under Water”, highlighting the mutual benefits of protecting both the marine environment and underwater heritage from the common pressures arising from ammunitions, ghost nets and eutrophication.
Chaired by Germany, HOD 59-2020 was attended by participants from all Contracting Parties, by Observers from Baltic Farmers’ Forum on Environment (BFFE), Baltic Sea Advisory Council (BSAC), Baltic Sea Parliamentary Conference (BSPC), Baltic Sea States Subregional Co-operation (BSSSC) & CPMR Baltic Sea Commission, Coalition Clean Baltic (CCB), Cruise Lines International Association Europe (CLIA Europe), Federation of European Aquaculture Producers (FEAP), Global Water Partnership Central and Eastern Europe and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) and by invited guests.
- Read the outcome of HOD 59-2020 and see all meeting documents